Some desert plants store water their leaves, stems, roots. have thick, waxy skin helps prevent water loss. desert plants small leaves help reduce evaporation.
 Many desert plants, as acacia creosote bush, small narrow leaves reduce area exposed the sun, reducing water loss. desert plants, as saguaro prickly pear cacti, replace leaves spines, provide shade reduce airflow the plant, minimizing water loss.
Many desert plants, as acacia creosote bush, small narrow leaves reduce area exposed the sun, reducing water loss. desert plants, as saguaro prickly pear cacti, replace leaves spines, provide shade reduce airflow the plant, minimizing water loss.
 Desert plants adapted their arid environment having or leaves. is in deserts, is scarcity water. By fewer leaves no leaves all, desert plants able reduce water loss transpiration. is important adaptation it helps conserve water survive water-scarce areas.
Desert plants adapted their arid environment having or leaves. is in deserts, is scarcity water. By fewer leaves no leaves all, desert plants able reduce water loss transpiration. is important adaptation it helps conserve water survive water-scarce areas.
 Desert plants afford lose water, therefore plants perform Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) photosynthesis carbon fixation. CAM photosynthesis, stomata remain closed the day open night absorb carbon dioxide, is stored the vacuoles malate. . of reduce evapotranspiration .
Desert plants afford lose water, therefore plants perform Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) photosynthesis carbon fixation. CAM photosynthesis, stomata remain closed the day open night absorb carbon dioxide, is stored the vacuoles malate. . of reduce evapotranspiration .
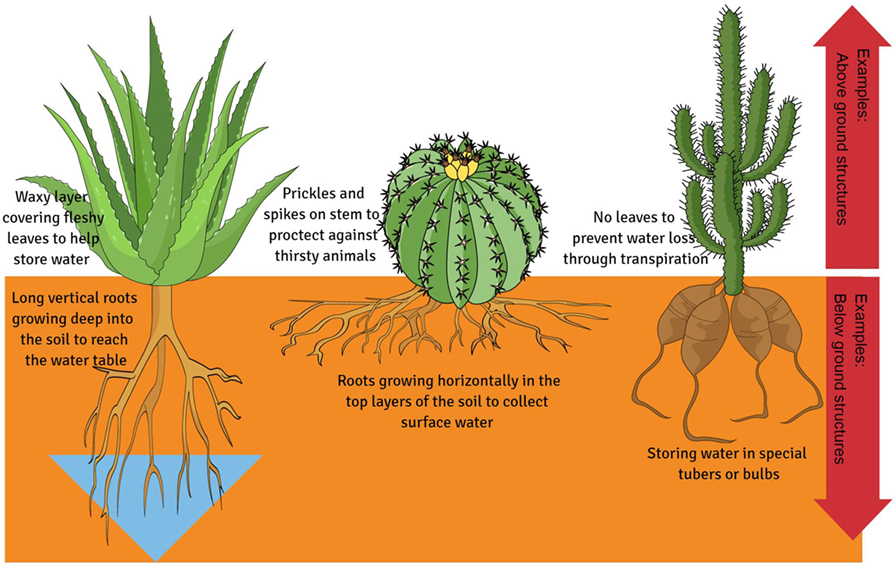 Excessive sunlight damage plant tissues, leading scorching water loss. combat this, desert plants leaves stems reflective surfaces. presence hairs, scales, a whitish coating bounce of sunlight away, reducing heat load the plant. Pale coloration, as silvery light green hues .
Excessive sunlight damage plant tissues, leading scorching water loss. combat this, desert plants leaves stems reflective surfaces. presence hairs, scales, a whitish coating bounce of sunlight away, reducing heat load the plant. Pale coloration, as silvery light green hues .
 The leaves the desert plants small-sized, may ribbon-like spiralled, are few numbers stomata lie deeply reduce loss water by transpiration the Calamagrostis plant. leaves the desert plants used storing water in cactus, leaves the desert plants surrounded a waxy layer prevent water loss by transpiration .
The leaves the desert plants small-sized, may ribbon-like spiralled, are few numbers stomata lie deeply reduce loss water by transpiration the Calamagrostis plant. leaves the desert plants used storing water in cactus, leaves the desert plants surrounded a waxy layer prevent water loss by transpiration .
 Many common desert shrubs plants characteristics help reduce water loss. adaptations include leaves a small surface area-to-volume ratio, as conifers grasses. plants, as cacti, evolved exist true leaves, others - including brittlebush burroweed - lose leaves .
Many common desert shrubs plants characteristics help reduce water loss. adaptations include leaves a small surface area-to-volume ratio, as conifers grasses. plants, as cacti, evolved exist true leaves, others - including brittlebush burroweed - lose leaves .
 The structural design these plants plays significant role their water storage capabilities. desert plants exhibit thick, waxy cuticle their surfaces, minimizes water loss evaporation. protective layer complemented a reduced number stomata, tiny openings leaves facilitate gas exchange.
The structural design these plants plays significant role their water storage capabilities. desert plants exhibit thick, waxy cuticle their surfaces, minimizes water loss evaporation. protective layer complemented a reduced number stomata, tiny openings leaves facilitate gas exchange.
 Desert plants protect in order survive not eaten animals. defend with physical defenses as spines, other defend with toxic chemicals. . Second, succulent spines reduce water loss. spines this breaking air flow, reducing evaporation, creating buffer zone .
Desert plants protect in order survive not eaten animals. defend with physical defenses as spines, other defend with toxic chemicals. . Second, succulent spines reduce water loss. spines this breaking air flow, reducing evaporation, creating buffer zone .
 Loss water a concern plants the desert; many plants adaptations their leaves avoid losing large quantities water. of leaf adaptations are: (1) hairy fuzzy leaves, (2) small leaves, (3) curled-up leaves, (4) waxcoated leaves, (5) green stems no leaves.
Loss water a concern plants the desert; many plants adaptations their leaves avoid losing large quantities water. of leaf adaptations are: (1) hairy fuzzy leaves, (2) small leaves, (3) curled-up leaves, (4) waxcoated leaves, (5) green stems no leaves.
 In desert plants, the rate of water loss gets reduced due to the
In desert plants, the rate of water loss gets reduced due to the

