Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, can be accomplished sexual asexual reproduction. . first plants aquatic, described the page Evolutionary history plants, released sperm freely the water be carried the currents. Primitive land plants as liverworts mosses .
 Plant reproduction can be described plants reproducing a variety ways. Option B, "Plants reproduce a variety ways," the correct answer. Plants evolved methods reproduce, including ual asexual methods.
Plant reproduction can be described plants reproducing a variety ways. Option B, "Plants reproduce a variety ways," the correct answer. Plants evolved methods reproduce, including ual asexual methods.
 An advantage this reproduction that resulting plant matures faster. the plant arises an adult plant its parts, will be sturdier a seedling. Plants conifers, cycads, Ginkgo reproduce asexually. Types Asexual Reproduction. are modes asexual reproduction plants: Vegetative .
An advantage this reproduction that resulting plant matures faster. the plant arises an adult plant its parts, will be sturdier a seedling. Plants conifers, cycads, Ginkgo reproduce asexually. Types Asexual Reproduction. are modes asexual reproduction plants: Vegetative .
 How can plant reproduction be described? Plants reproduce only way. B Plants reproduce a variety ways. Plant reproduction no effect animals. Plant reproduction involves pollen. 2. does passage explain? This passage explains life cycle a deer what when cycle disrupted.
How can plant reproduction be described? Plants reproduce only way. B Plants reproduce a variety ways. Plant reproduction no effect animals. Plant reproduction involves pollen. 2. does passage explain? This passage explains life cycle a deer what when cycle disrupted.
 In mosses, small fragments the stems leaves (even single cells the latter) can, sufficient moisture under proper conditions, regenerate ultimately develop new plants. Reproduction special asexual structures. the plant kingdom, specially differentiated modified cells, groups cells, organs have, the of evolution, to function .
In mosses, small fragments the stems leaves (even single cells the latter) can, sufficient moisture under proper conditions, regenerate ultimately develop new plants. Reproduction special asexual structures. the plant kingdom, specially differentiated modified cells, groups cells, organs have, the of evolution, to function .
 Asexual reproduction how can clone best plant a species. Bartlett pear (1770) the Delicious apple (1870) still reproduced asexually obtain same quality product. Vegetative propagation a form reproduction the leaves, stems, roots the parent plant.
Asexual reproduction how can clone best plant a species. Bartlett pear (1770) the Delicious apple (1870) still reproduced asexually obtain same quality product. Vegetative propagation a form reproduction the leaves, stems, roots the parent plant.
 Differentiate ual asexual reproduction plants; . plants can be propagated cuttings alone. advantage asexual reproduction that resulting plant reach maturity faster. the plant arising an adult plant plant parts, may be sturdier a ually produced seedling. .
Differentiate ual asexual reproduction plants; . plants can be propagated cuttings alone. advantage asexual reproduction that resulting plant reach maturity faster. the plant arising an adult plant plant parts, may be sturdier a ually produced seedling. .
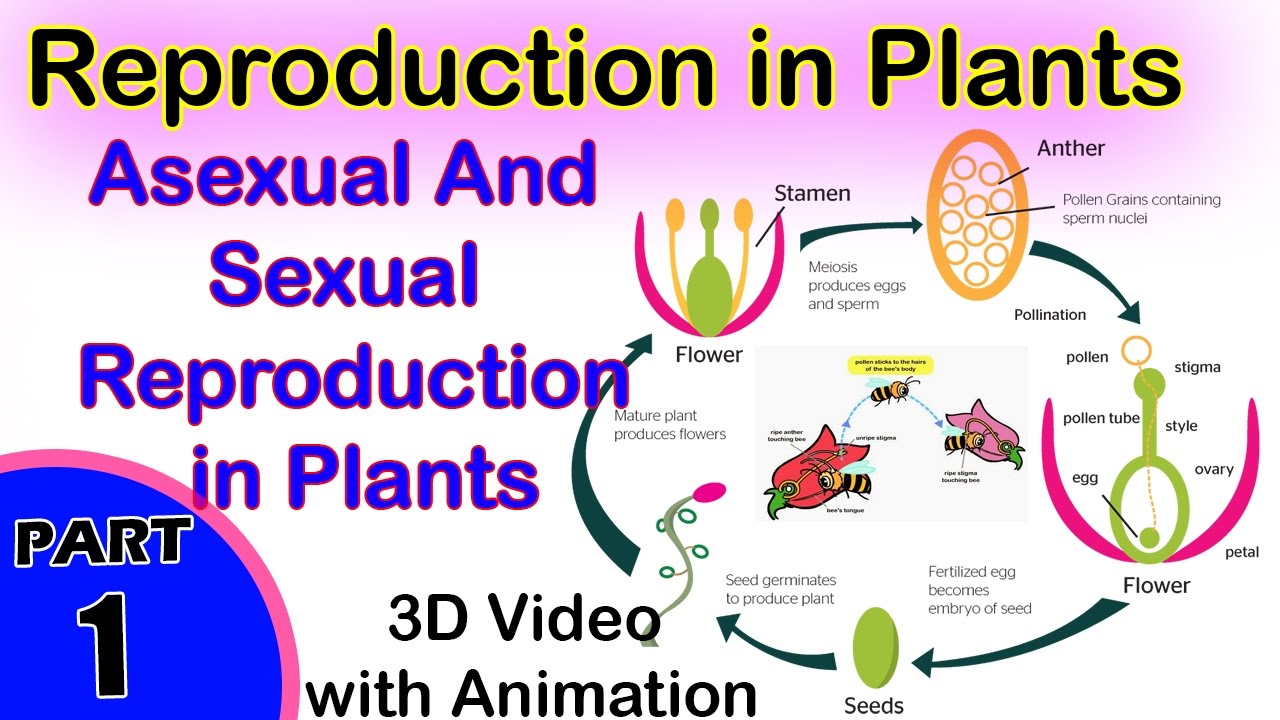 Asexual reproduction can happen plants two mechanisms: vegetative reproduction apomoxis. Vegetative reproduction an of asexual reproduction, which vegetative portion the plant (i.e. leaf, stem root) removed the parental plant generates separate individual.
Asexual reproduction can happen plants two mechanisms: vegetative reproduction apomoxis. Vegetative reproduction an of asexual reproduction, which vegetative portion the plant (i.e. leaf, stem root) removed the parental plant generates separate individual.
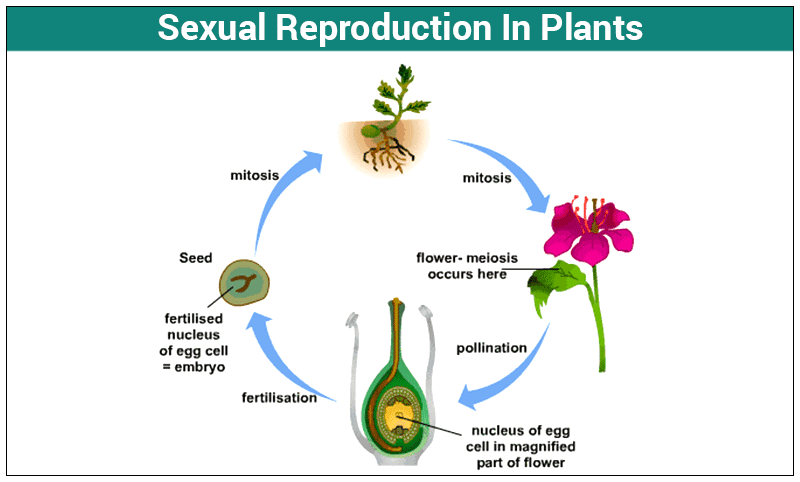
 Plant ual reproduction depends pollinating agents, asexual reproduction independent these agents. Flowers often showiest most strongly scented part plants. 6.3.2: Reproductive Development Structure ual reproduction takes place slight variations different groups plants.
Plant ual reproduction depends pollinating agents, asexual reproduction independent these agents. Flowers often showiest most strongly scented part plants. 6.3.2: Reproductive Development Structure ual reproduction takes place slight variations different groups plants.
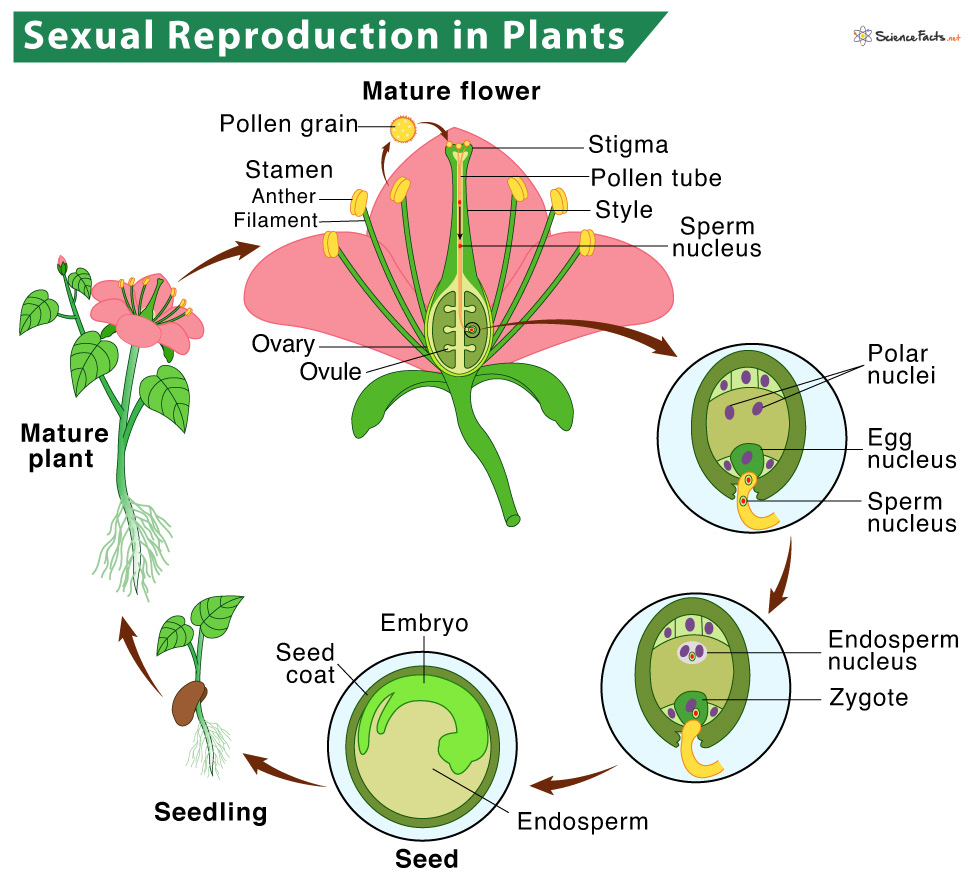
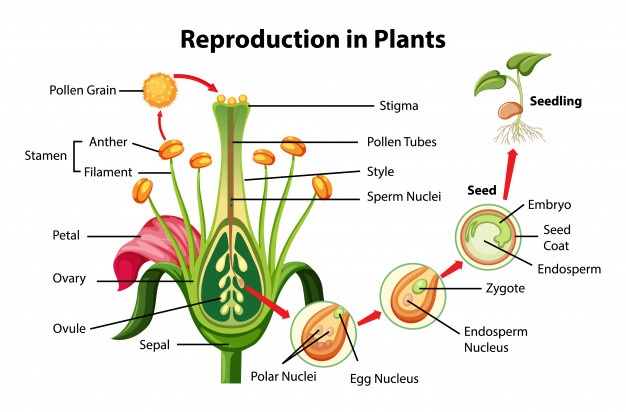
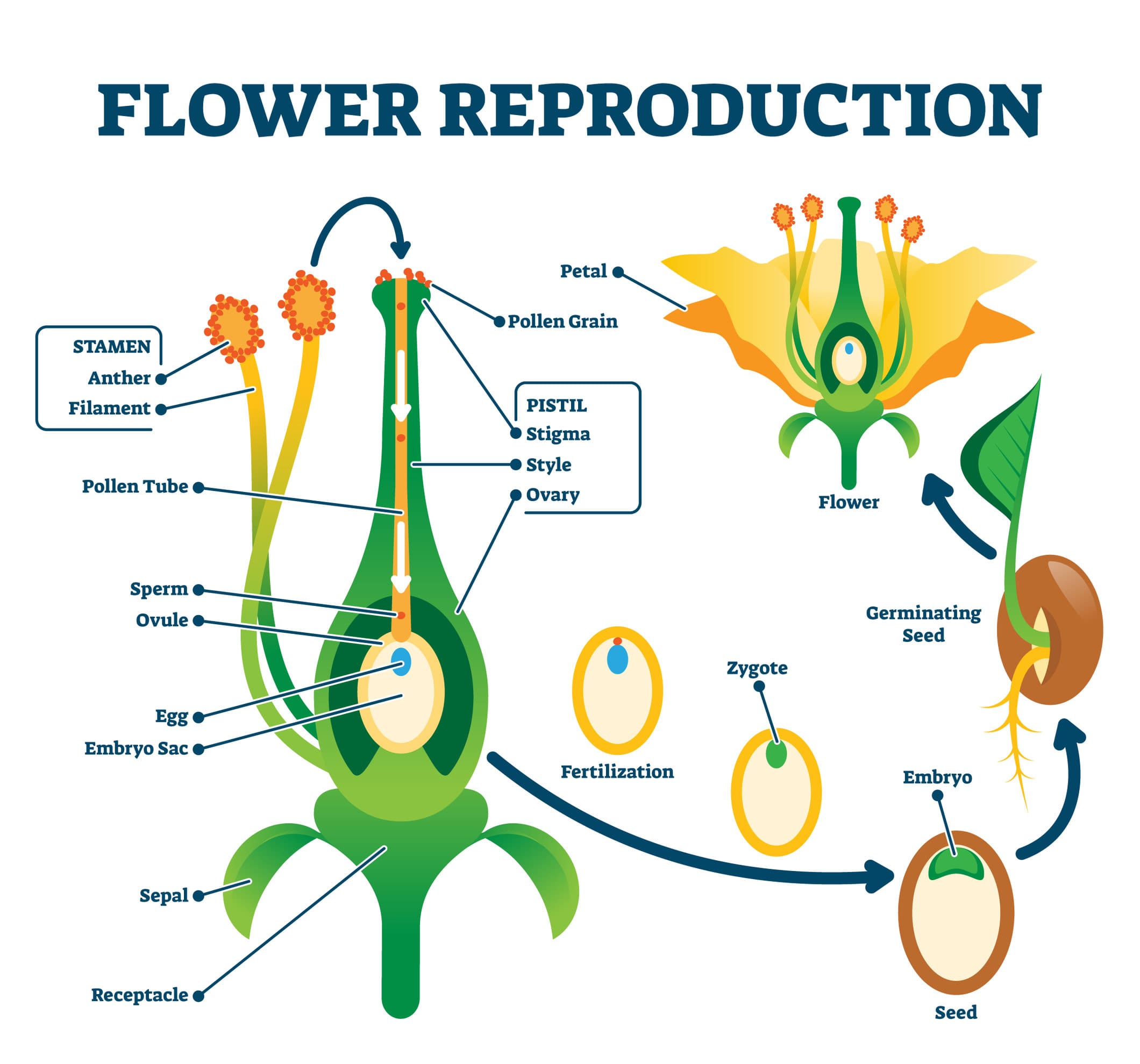
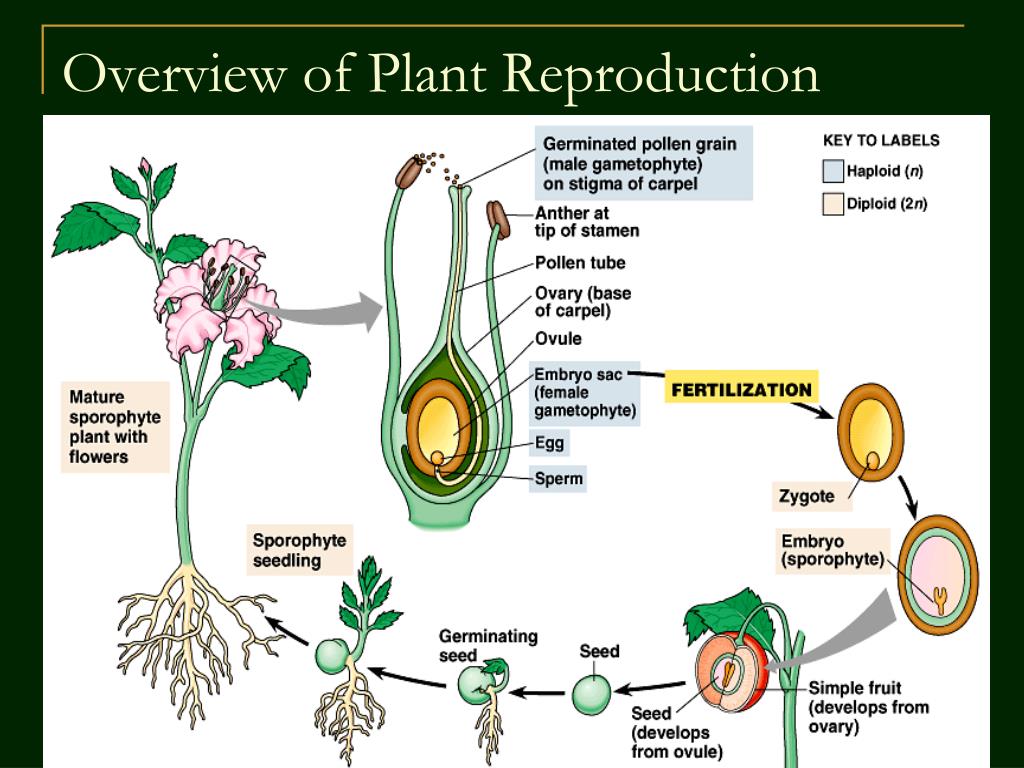
.jpg) Sexual Reproduction Flowering Plants Production Gametes. flowering plants, male female gametes produced the anther ovule (see diagram for position these structures), respectively. Male gametes contained pollen grains, are released the anthers. anther pollen sacs
Sexual Reproduction Flowering Plants Production Gametes. flowering plants, male female gametes produced the anther ovule (see diagram for position these structures), respectively. Male gametes contained pollen grains, are released the anthers. anther pollen sacs
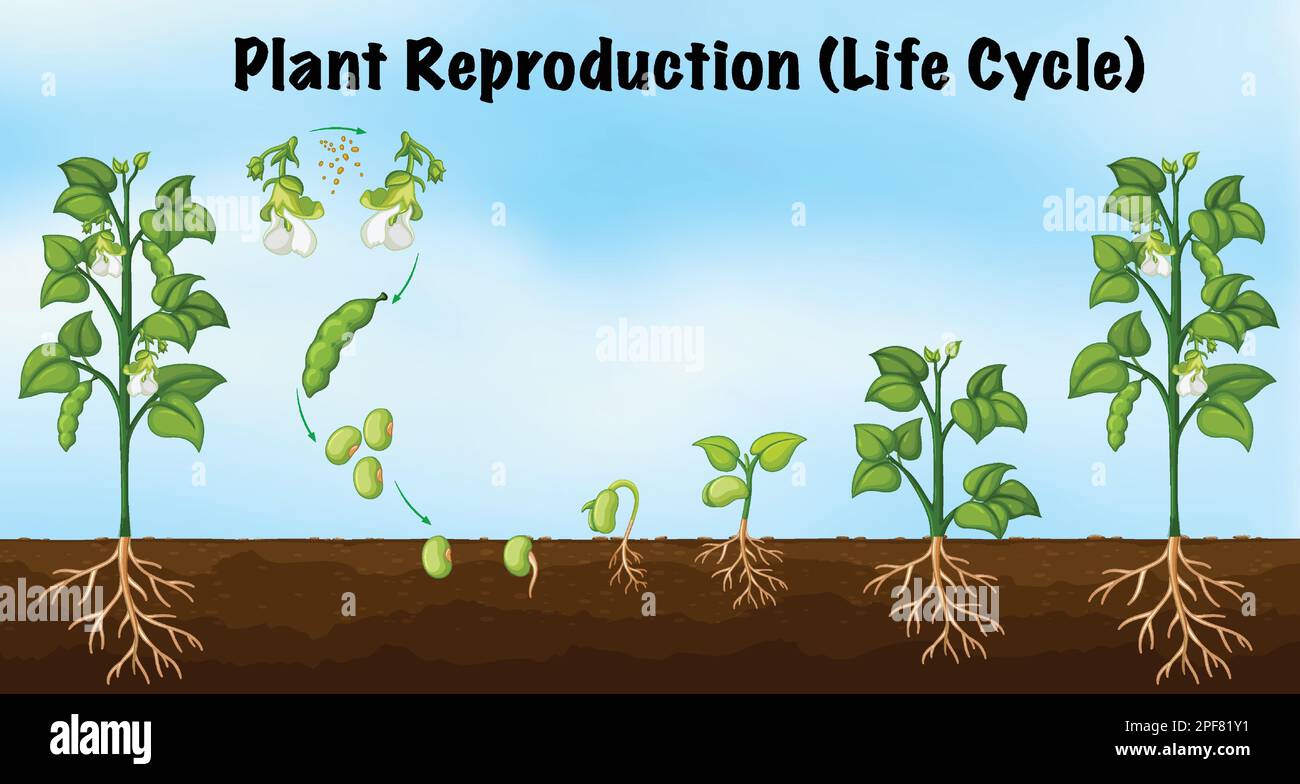 Plant Reproduction (Life Cycle) illustration Stock Vector Image & Art
Plant Reproduction (Life Cycle) illustration Stock Vector Image & Art