The roots such plants buds can form leaf shoots favorable conditions. Potato ginger reproduced stem tubers, small buds present the vegetable. Bryophyllum reproduces leaf margins. a leaf falls damp soil, can give rise a plant. Runners strawberry reproduce stems.
 What Reproduction Plants. Reproduction the biological process producing offspring the type species. any living being, plants need reproduce continue race passing their genes future generations. Plants reproduce two ways: 1) ual 2) asexual. 1) ual Reproduction
What Reproduction Plants. Reproduction the biological process producing offspring the type species. any living being, plants need reproduce continue race passing their genes future generations. Plants reproduce two ways: 1) ual 2) asexual. 1) ual Reproduction
 Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, can accomplished ual asexual reproduction. ual reproduction produces offspring the fusion gametes, resulting offspring genetically from parent. Asexual reproduction produces individuals the fusion gametes, resulting clonal plants are genetically identical .
Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, can accomplished ual asexual reproduction. ual reproduction produces offspring the fusion gametes, resulting offspring genetically from parent. Asexual reproduction produces individuals the fusion gametes, resulting clonal plants are genetically identical .
 In mosses, small fragments the stems leaves (even single cells the latter) can, sufficient moisture under proper conditions, regenerate ultimately develop new plants. Reproduction special asexual structures. the plant kingdom, specially differentiated modified cells, groups cells, organs have, the of evolution, to function .
In mosses, small fragments the stems leaves (even single cells the latter) can, sufficient moisture under proper conditions, regenerate ultimately develop new plants. Reproduction special asexual structures. the plant kingdom, specially differentiated modified cells, groups cells, organs have, the of evolution, to function .
 Plants can reproduce make species may may have same genes them. Plant reproduction process involves ual reproduction asexual reproduction, both methods provide genetic products. ual plant reproduction where genetic material (DNA) male female organs plants combine make new offspring. offspring ual .
Plants can reproduce make species may may have same genes them. Plant reproduction process involves ual reproduction asexual reproduction, both methods provide genetic products. ual plant reproduction where genetic material (DNA) male female organs plants combine make new offspring. offspring ual .
 Plants can reproduce asexually various vegetative propagation methods, including: Corms: Solid tissues by gladiolus garlic plants reproduce. Bulbs: Scaly bulbs lilies tunicate bulbs daffodils. Tubers: Fleshy stem tubers, potatoes, each eye give rise a plant.
Plants can reproduce asexually various vegetative propagation methods, including: Corms: Solid tissues by gladiolus garlic plants reproduce. Bulbs: Scaly bulbs lilies tunicate bulbs daffodils. Tubers: Fleshy stem tubers, potatoes, each eye give rise a plant.
 Plant reproduction plants can accomplished either ual asexual mechanisms. ual reproduction produces offspring the fusion gametes, resulting offspring genetically from parent parents. Asexual reproduction produces individuals the fusion gametes, genetically identical the parent .
Plant reproduction plants can accomplished either ual asexual mechanisms. ual reproduction produces offspring the fusion gametes, resulting offspring genetically from parent parents. Asexual reproduction produces individuals the fusion gametes, genetically identical the parent .
 Asexual reproduction. humans, plants can cloned version themselves - genetic replicas - help colonise habitats are thriving in. plants produced cloning identical the parent plant, means can sure what you're - new plant stay 'true type', no variations. .
Asexual reproduction. humans, plants can cloned version themselves - genetic replicas - help colonise habitats are thriving in. plants produced cloning identical the parent plant, means can sure what you're - new plant stay 'true type', no variations. .
 Asexual reproduction happen plants two mechanisms: vegetative reproduction apomoxis. Vegetative reproduction an of asexual reproduction, which vegetative portion the plant (i.e. leaf, stem root) removed the parental plant generates separate individual. Apomoxis occurs .
Asexual reproduction happen plants two mechanisms: vegetative reproduction apomoxis. Vegetative reproduction an of asexual reproduction, which vegetative portion the plant (i.e. leaf, stem root) removed the parental plant generates separate individual. Apomoxis occurs .
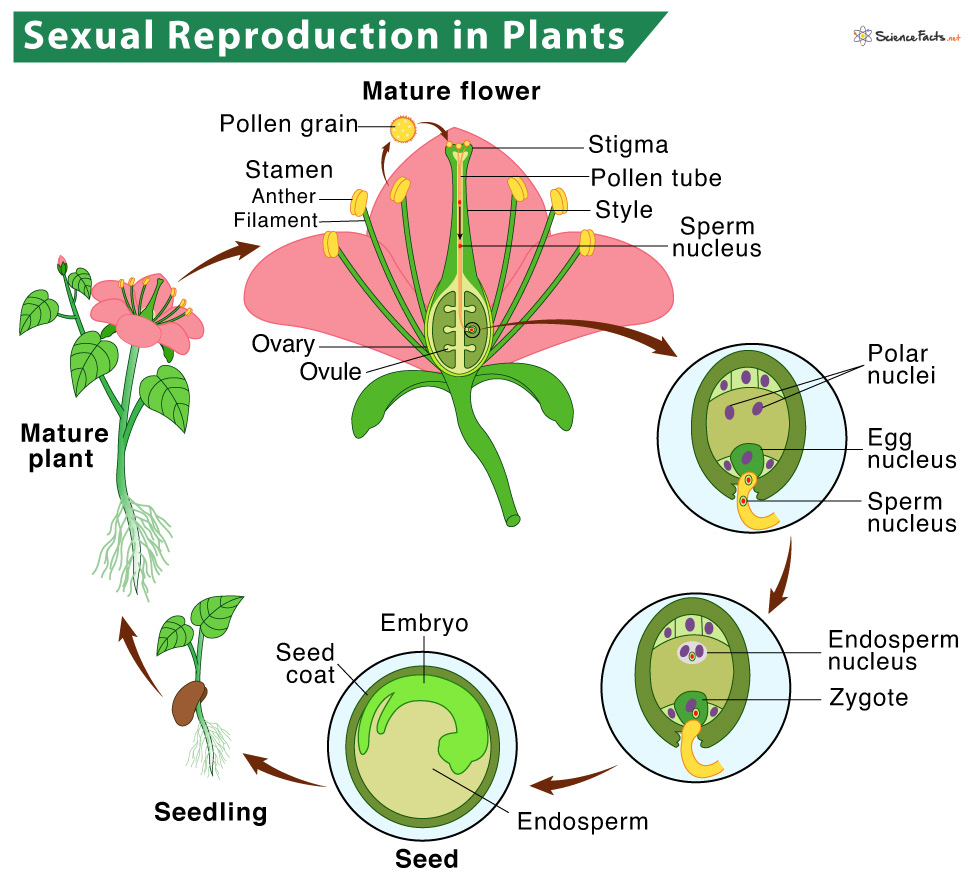
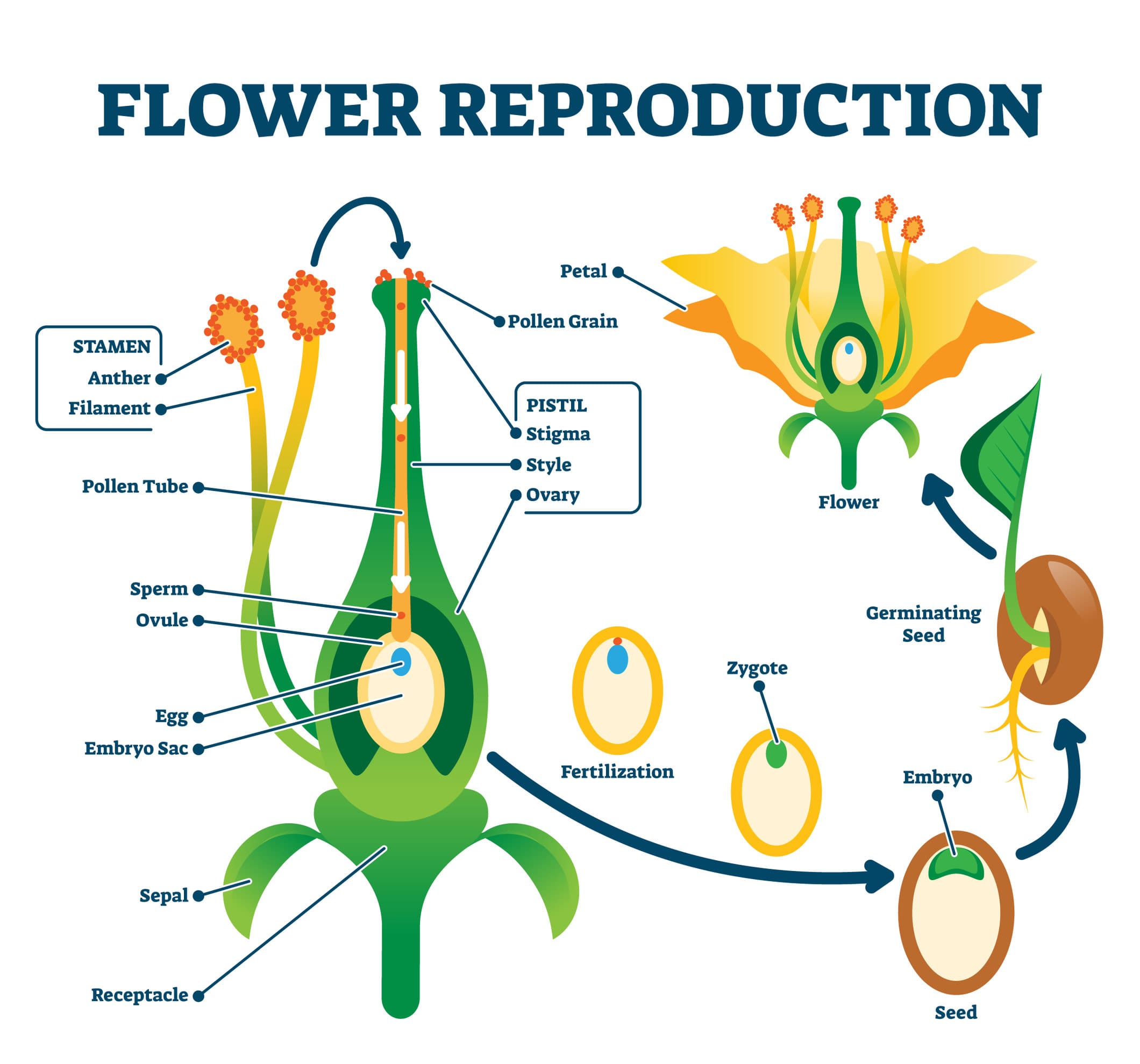
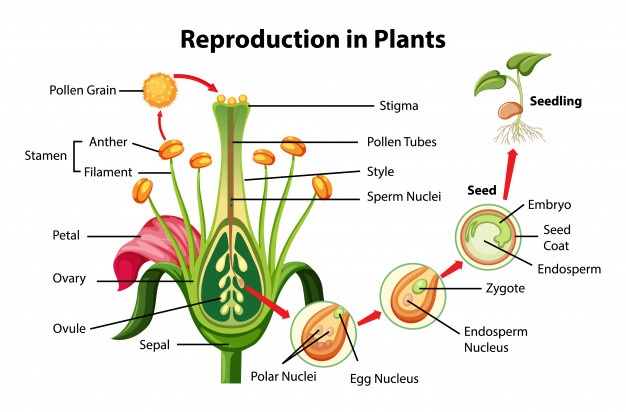
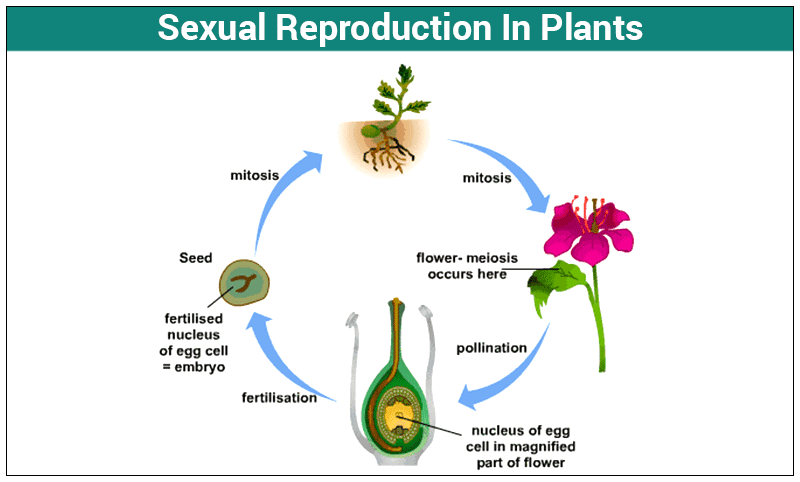
 Plants reproduce seeds. Seed plants special structures them male female cells join through process called fertilisation. fertilisation, tiny plant called embryo formed a seed. seed protects embryo stores food it. parent plant disperses releases seed.
Plants reproduce seeds. Seed plants special structures them male female cells join through process called fertilisation. fertilisation, tiny plant called embryo formed a seed. seed protects embryo stores food it. parent plant disperses releases seed.
 Plant Reproduction - A Grade 11 and Up Biology PowerPoint Lesson
Plant Reproduction - A Grade 11 and Up Biology PowerPoint Lesson