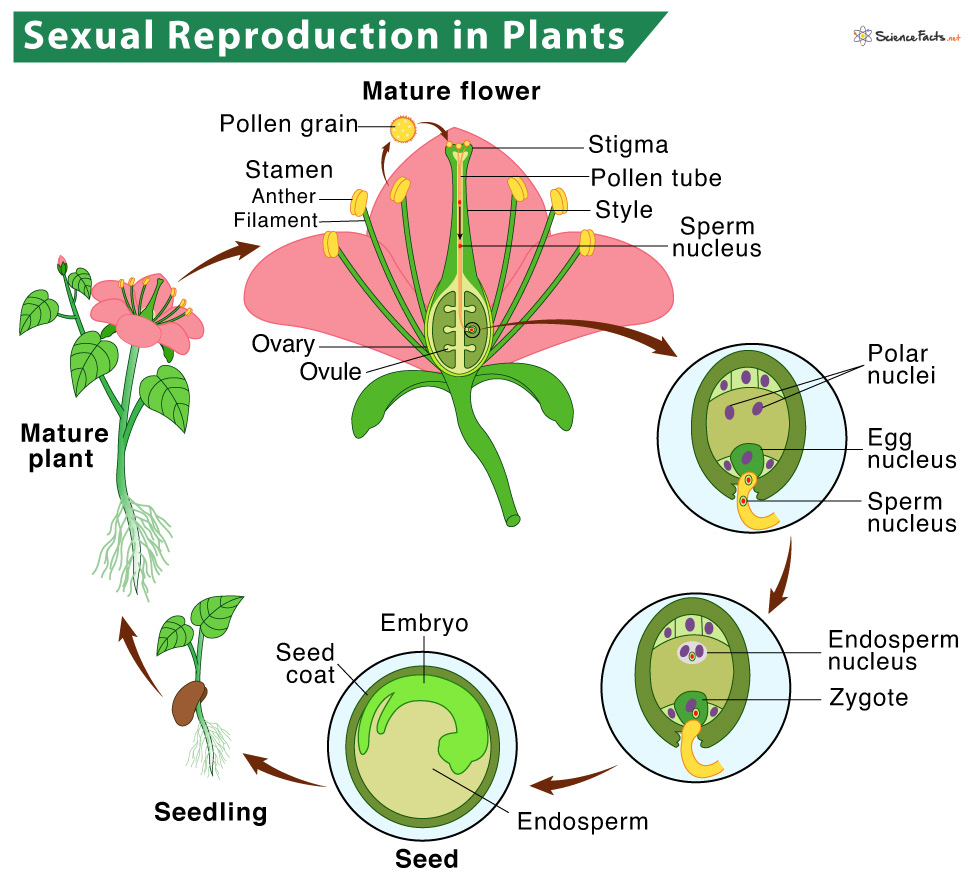
Learn sexual asexual reproduction plants, the parts a flower involved sexual reproduction. Find how pollination, pollinators, seeds work plant reproduction.
 What Reproduction Plants. Reproduction the biological process producing offspring the type species. any living being, plants need reproduce continue race passing their genes future generations. Plants reproduce two ways: 1) ual 2) asexual. 1) ual Reproduction
What Reproduction Plants. Reproduction the biological process producing offspring the type species. any living being, plants need reproduce continue race passing their genes future generations. Plants reproduce two ways: 1) ual 2) asexual. 1) ual Reproduction
 Plants germinate, sprout, root, leaf and bloom through process mitosis occurring the cellular level. of action in meristematic tissue undifferentiated cells capable specialization. Vascular plants, flowering plants, ferns, cacti mosses among thousands plant groups the world capable perpetual plant reproduction.
Plants germinate, sprout, root, leaf and bloom through process mitosis occurring the cellular level. of action in meristematic tissue undifferentiated cells capable specialization. Vascular plants, flowering plants, ferns, cacti mosses among thousands plant groups the world capable perpetual plant reproduction.
 Learn how plants reproduce asexually ually, examples different plant groups. Asexual reproduction involves fragments special structures, ual reproduction involves gametes fertilization.
Learn how plants reproduce asexually ually, examples different plant groups. Asexual reproduction involves fragments special structures, ual reproduction involves gametes fertilization.
 Learn how plants reproduce ually asexually, the differences them. Find about pollination, fertilization, seeds, fruits, various methods asexual reproduction.
Learn how plants reproduce ually asexually, the differences them. Find about pollination, fertilization, seeds, fruits, various methods asexual reproduction.
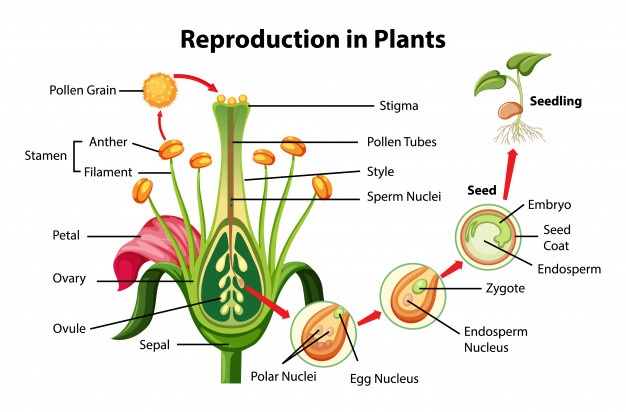
 In flowering plants animals, reproductive cells, known gametes, half number chromosomes in normal adult cells. fusion gametes restores normal .
In flowering plants animals, reproductive cells, known gametes, half number chromosomes in normal adult cells. fusion gametes restores normal .
 Differentiate ual asexual reproduction plants; . Altogether, process circulates water all cells the plant, facilitates movement sugars, minerals, hormones, more essential elements cells. 1. Water diffuses root cells. 2. Due the properties adhesion cohesion, water molecules .
Differentiate ual asexual reproduction plants; . Altogether, process circulates water all cells the plant, facilitates movement sugars, minerals, hormones, more essential elements cells. 1. Water diffuses root cells. 2. Due the properties adhesion cohesion, water molecules .
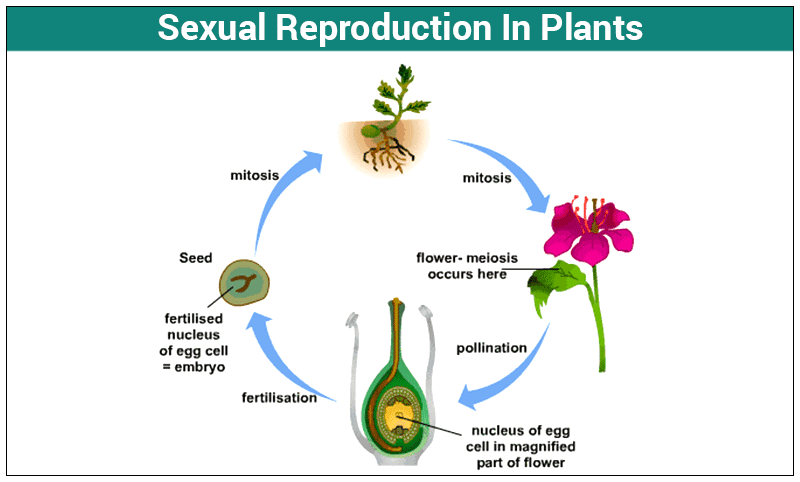
 Sexual reproduction the cellular level generally involves following phenomena: union cells their nuclei, concomitant association their chromosomes, contain genes, the nuclear division called meiosis.The cells called gametes, the product their union a zygote.All gametes normally haploid (having single set chromosomes) .
Sexual reproduction the cellular level generally involves following phenomena: union cells their nuclei, concomitant association their chromosomes, contain genes, the nuclear division called meiosis.The cells called gametes, the product their union a zygote.All gametes normally haploid (having single set chromosomes) .
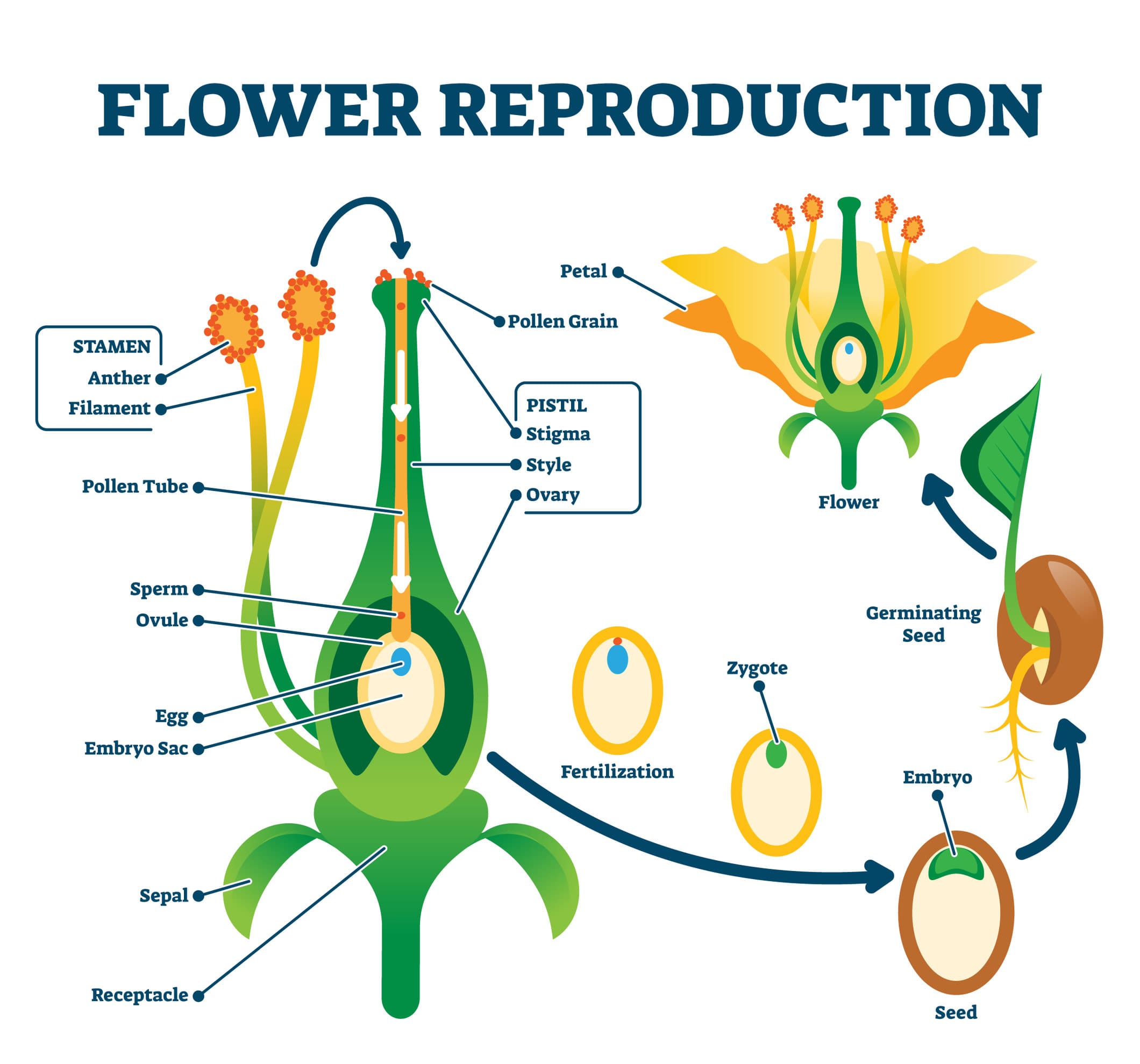
 Some plants reproduce ually, others asexually, contrast animal species, rely exclusively ual reproduction. Plant ual reproduction depends pollinating agents, asexual reproduction independent these agents. Flowers often showiest most strongly scented part plants. 6.3.2 .
Some plants reproduce ually, others asexually, contrast animal species, rely exclusively ual reproduction. Plant ual reproduction depends pollinating agents, asexual reproduction independent these agents. Flowers often showiest most strongly scented part plants. 6.3.2 .
 A plant cell the basic unit all plants. Plant cells, animal cells, eukaryotic, meaning have membrane-bound nucleus organelles. characteristic cell wall composed cellulose, they chloroplasts photosynthesis. . How do plant cells reproduce grow? is significance the nucleus .
A plant cell the basic unit all plants. Plant cells, animal cells, eukaryotic, meaning have membrane-bound nucleus organelles. characteristic cell wall composed cellulose, they chloroplasts photosynthesis. . How do plant cells reproduce grow? is significance the nucleus .
 Sexual Reproduction · Biology
Sexual Reproduction · Biology