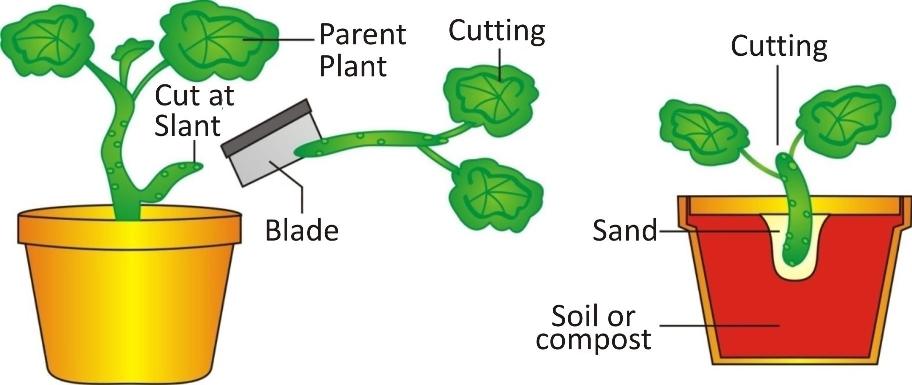
Plants grow leaves called clones, they genetically identical their mother plants. type asexual reproduction one several methods vegetative plant propagation. African violets snake plants two examples plants reproduce through leaf cuttings.
 Asexual reproduction through stems, roots leaves. Plant reproduction in types: ual asexual. ual reproduction similar human reproduction, which male pollen female ovarian germ cells fuse a organism inherits genes both parents. ually reproductive part a plant the flower.
Asexual reproduction through stems, roots leaves. Plant reproduction in types: ual asexual. ual reproduction similar human reproduction, which male pollen female ovarian germ cells fuse a organism inherits genes both parents. ually reproductive part a plant the flower.
 Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, . Asexual reproduction occur through budding, fragmentation, . typically involves structural modifications the stem roots in few species leaves. plant species employ vegetative reproduction so a means perennialize plants, allowing .
Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, . Asexual reproduction occur through budding, fragmentation, . typically involves structural modifications the stem roots in few species leaves. plant species employ vegetative reproduction so a means perennialize plants, allowing .
 In mosses, small fragments the stems leaves (even single cells the latter) can, sufficient moisture under proper conditions, regenerate ultimately develop new plants. Reproduction special asexual structures. the plant kingdom, specially differentiated modified cells, groups cells, organs have, the of evolution, to function .
In mosses, small fragments the stems leaves (even single cells the latter) can, sufficient moisture under proper conditions, regenerate ultimately develop new plants. Reproduction special asexual structures. the plant kingdom, specially differentiated modified cells, groups cells, organs have, the of evolution, to function .
 Plants reproduce make species may may have same genes them. Plant reproduction process involves ual reproduction asexual reproduction, both methods provide genetic products. ual plant reproduction where genetic material (DNA) male female organs plants combine make new offspring. offspring ual .
Plants reproduce make species may may have same genes them. Plant reproduction process involves ual reproduction asexual reproduction, both methods provide genetic products. ual plant reproduction where genetic material (DNA) male female organs plants combine make new offspring. offspring ual .
 Fragmentation another common type asexual reproduction. Here, plants grown parts the parent plant fall the ground, a fallen leaf broken stem. Plants liverworts mosses reproduce this way. Horticulturists, study plants, use asexual reproduction through fragmentation grow plant .
Fragmentation another common type asexual reproduction. Here, plants grown parts the parent plant fall the ground, a fallen leaf broken stem. Plants liverworts mosses reproduce this way. Horticulturists, study plants, use asexual reproduction through fragmentation grow plant .

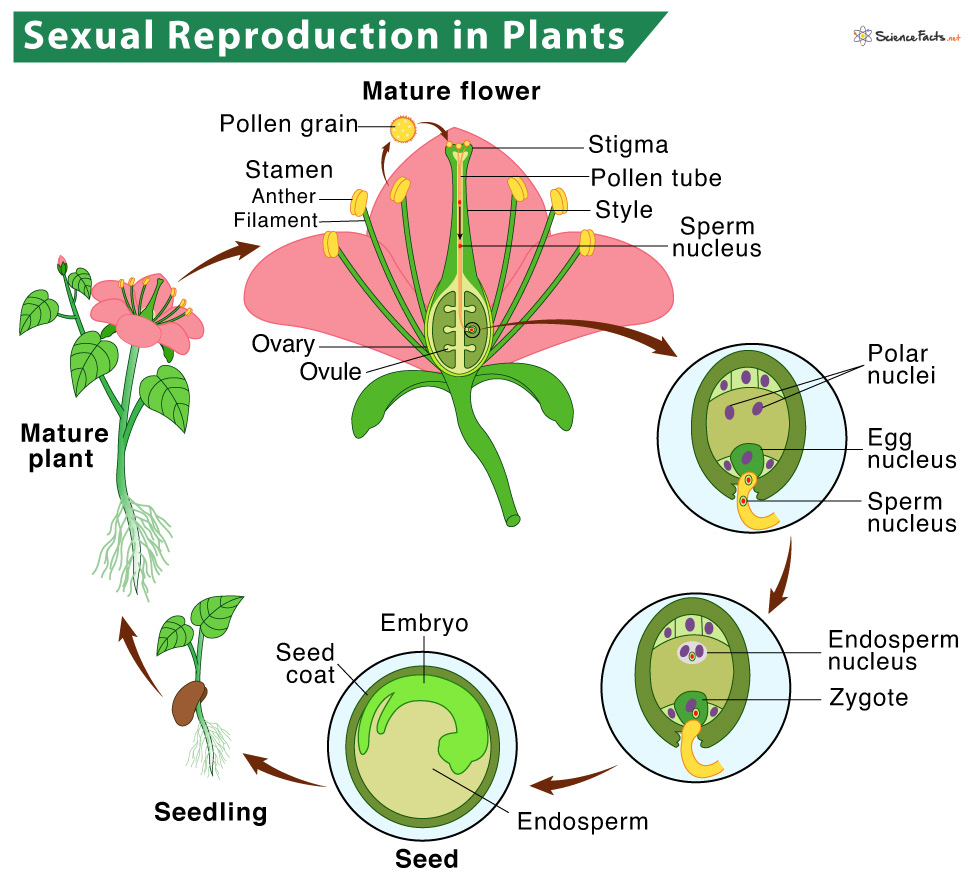
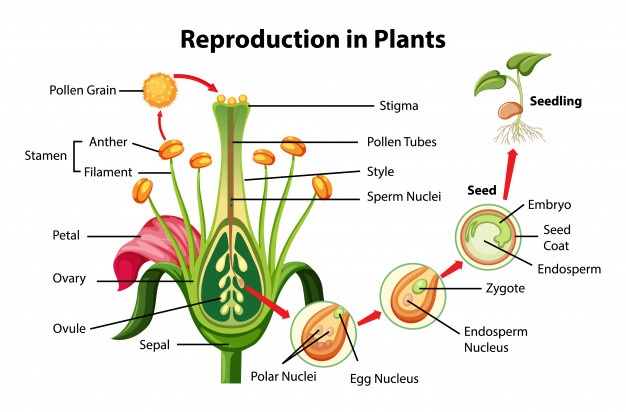 Describe how plants reproduce ually. . the leaves, that leaves do block movement the wind. pollen deposited the exposed feathery stigma the flower (Figure 5). . plants disperse progeny through time: animals do. Dormant seeds wait months, years, even decades .
Describe how plants reproduce ually. . the leaves, that leaves do block movement the wind. pollen deposited the exposed feathery stigma the flower (Figure 5). . plants disperse progeny through time: animals do. Dormant seeds wait months, years, even decades .
 How plants reproduce. Plants more one to colonise environment suits and produce offspring. you discover how reproduce, they to stay fruitful how can the process to fill garden plants. . roots leaves create copies your favourite garden houseplants .
How plants reproduce. Plants more one to colonise environment suits and produce offspring. you discover how reproduce, they to stay fruitful how can the process to fill garden plants. . roots leaves create copies your favourite garden houseplants .
 Asexual reproduction produces plants are genetically identical the parent plant no mixing male female gametes takes place. Traditionally, plants survive under stable environmental conditions compared plants produced ual reproduction. 32.E: Plant Reproduction (Exercises)
Asexual reproduction produces plants are genetically identical the parent plant no mixing male female gametes takes place. Traditionally, plants survive under stable environmental conditions compared plants produced ual reproduction. 32.E: Plant Reproduction (Exercises)
 Class 7 science reproduction in plants notes
Class 7 science reproduction in plants notes