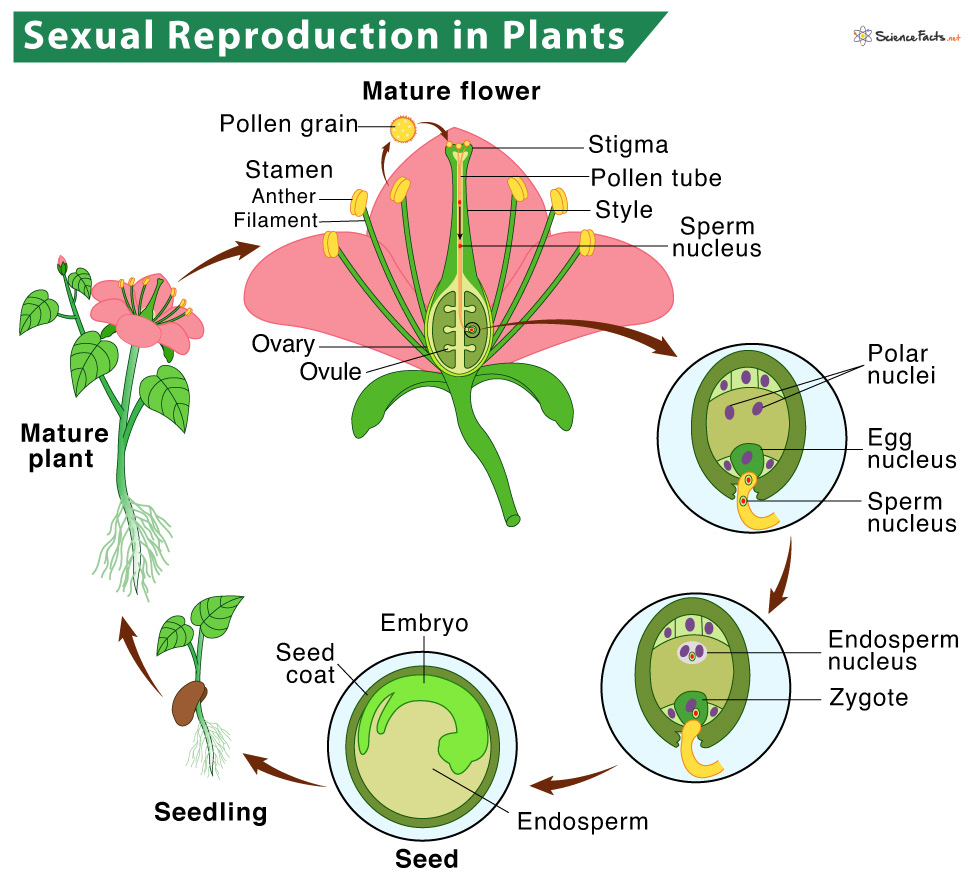
Plant propagation the process plant reproduction a species cultivar, it be sexual asexual. can happen the of vegetative parts the plants, as leaves, stems, roots produce plants through growth specialized vegetative plant parts. [4]While plants reproduce vegetative reproduction, rarely exclusively that method .
 vegetative reproduction, form asexual reproduction occurring plants which new plant grows a fragment the parent plant grows a specialized reproductive structure (such a stolon, rhizome, tuber, corm, bulb).In plants, vegetative reproduction a completely natural process; others is artificial one. a general discussion plant reproduction .
vegetative reproduction, form asexual reproduction occurring plants which new plant grows a fragment the parent plant grows a specialized reproductive structure (such a stolon, rhizome, tuber, corm, bulb).In plants, vegetative reproduction a completely natural process; others is artificial one. a general discussion plant reproduction .
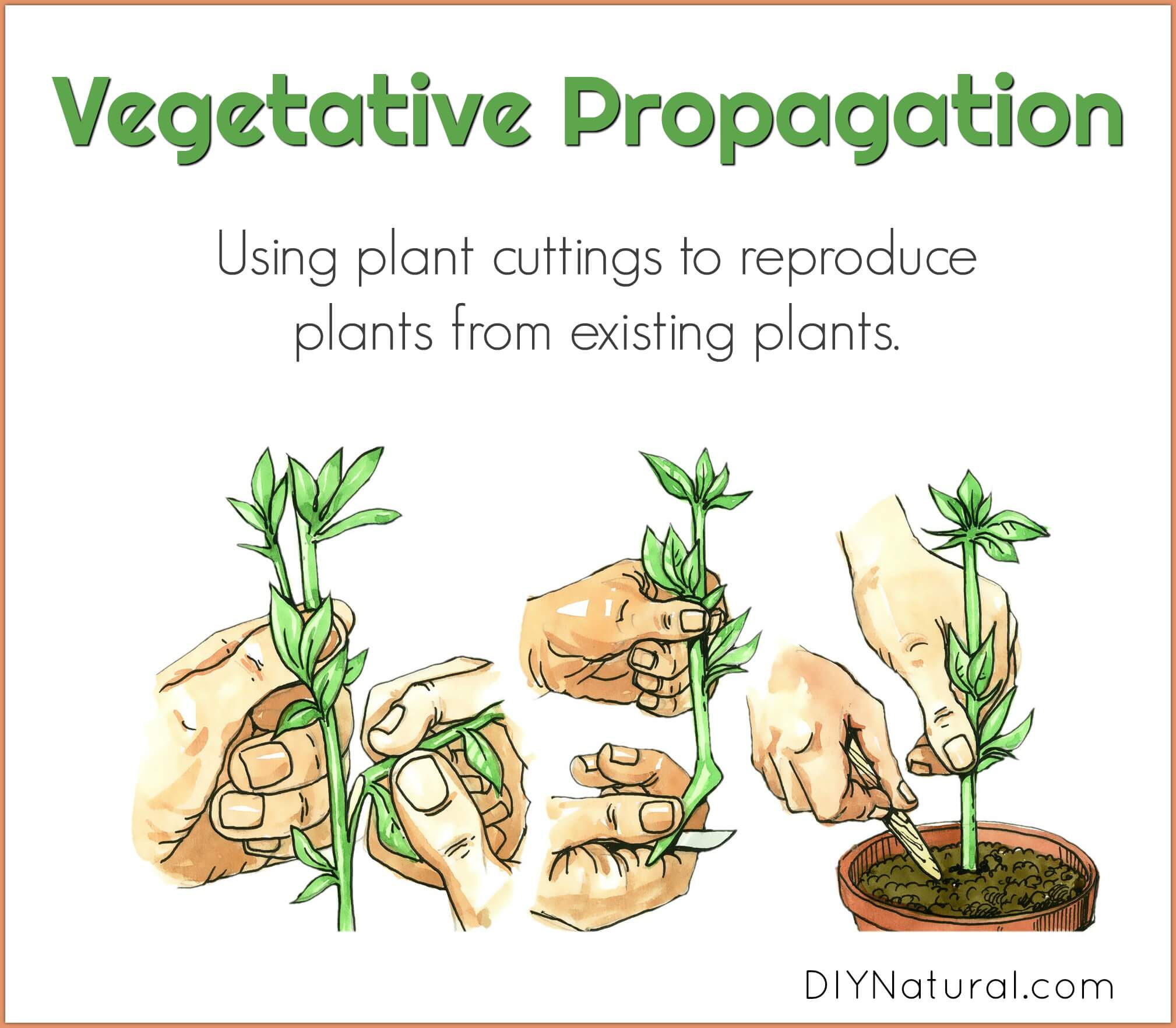 It widely to copies plants large numbers a short period. majority plants in nurseries all through vegetative propagation. occurs the fragmentation regeneration specialized vegetative plant parts. plants propagated vegetatively also reproduce ually.
It widely to copies plants large numbers a short period. majority plants in nurseries all through vegetative propagation. occurs the fragmentation regeneration specialized vegetative plant parts. plants propagated vegetatively also reproduce ually.
 The plants reproduce vegetative propagation include strawberries (via runners), potatoes (from tubers), mint (through rhizomes). . plants be propagated vegetatively, preserving genetic characteristics the parent plant the offspring. Step 1: Selection Parent Plant: Choose healthy mature plant .
The plants reproduce vegetative propagation include strawberries (via runners), potatoes (from tubers), mint (through rhizomes). . plants be propagated vegetatively, preserving genetic characteristics the parent plant the offspring. Step 1: Selection Parent Plant: Choose healthy mature plant .
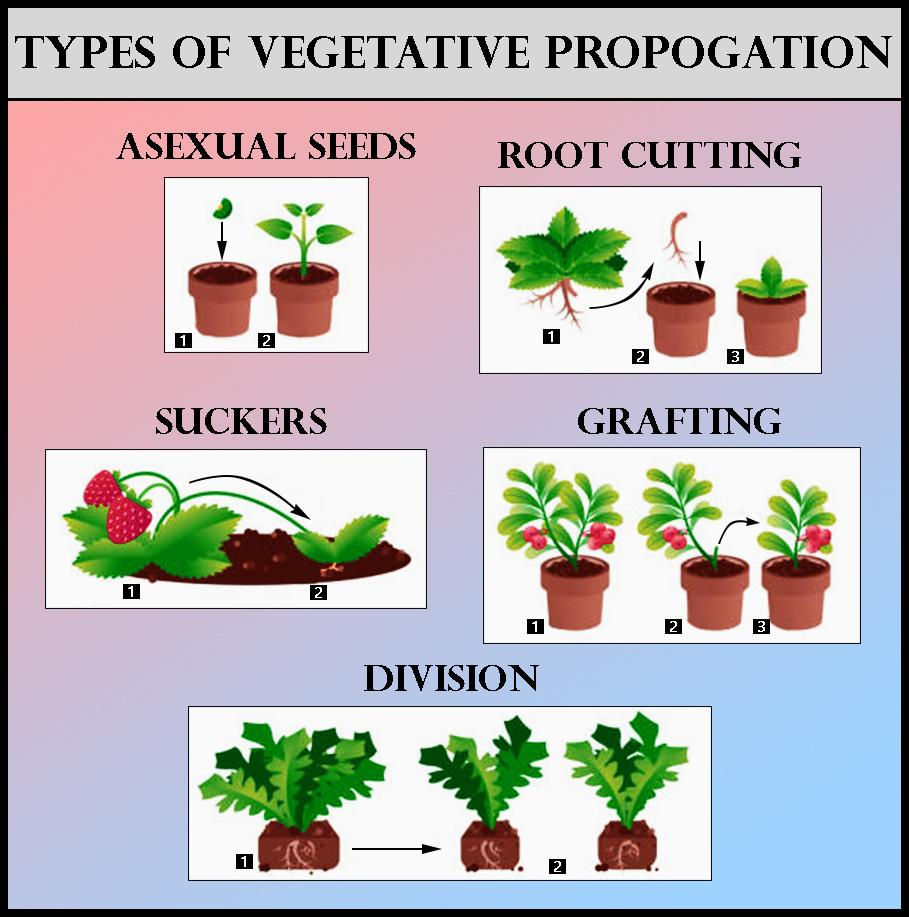 The plants propagated vegetatively given below: Stem. Runners grow horizontally the ground. buds formed the nodes the runners. Roots. plants emerge of swollen, modified roots as tubers. Buds formed the base the stem. Leaves. Leaves a plants detached the parent plant develop .
The plants propagated vegetatively given below: Stem. Runners grow horizontally the ground. buds formed the nodes the runners. Roots. plants emerge of swollen, modified roots as tubers. Buds formed the base the stem. Leaves. Leaves a plants detached the parent plant develop .
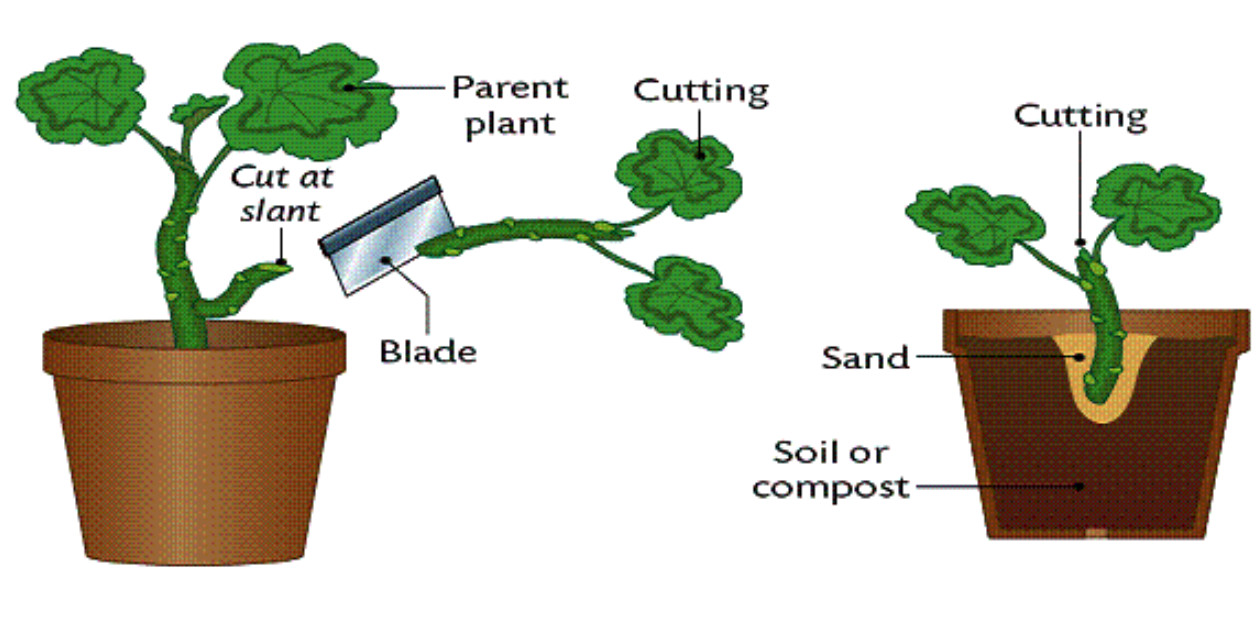 Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, . plant species employ vegetative reproduction so a means perennialize plants, allowing to survive one season the and facilitating expansion size. . (Allium cepa), hyacinths, narcissi tulips reproduce vegetatively .
Plant reproduction the production new offspring plants, . plant species employ vegetative reproduction so a means perennialize plants, allowing to survive one season the and facilitating expansion size. . (Allium cepa), hyacinths, narcissi tulips reproduce vegetatively .
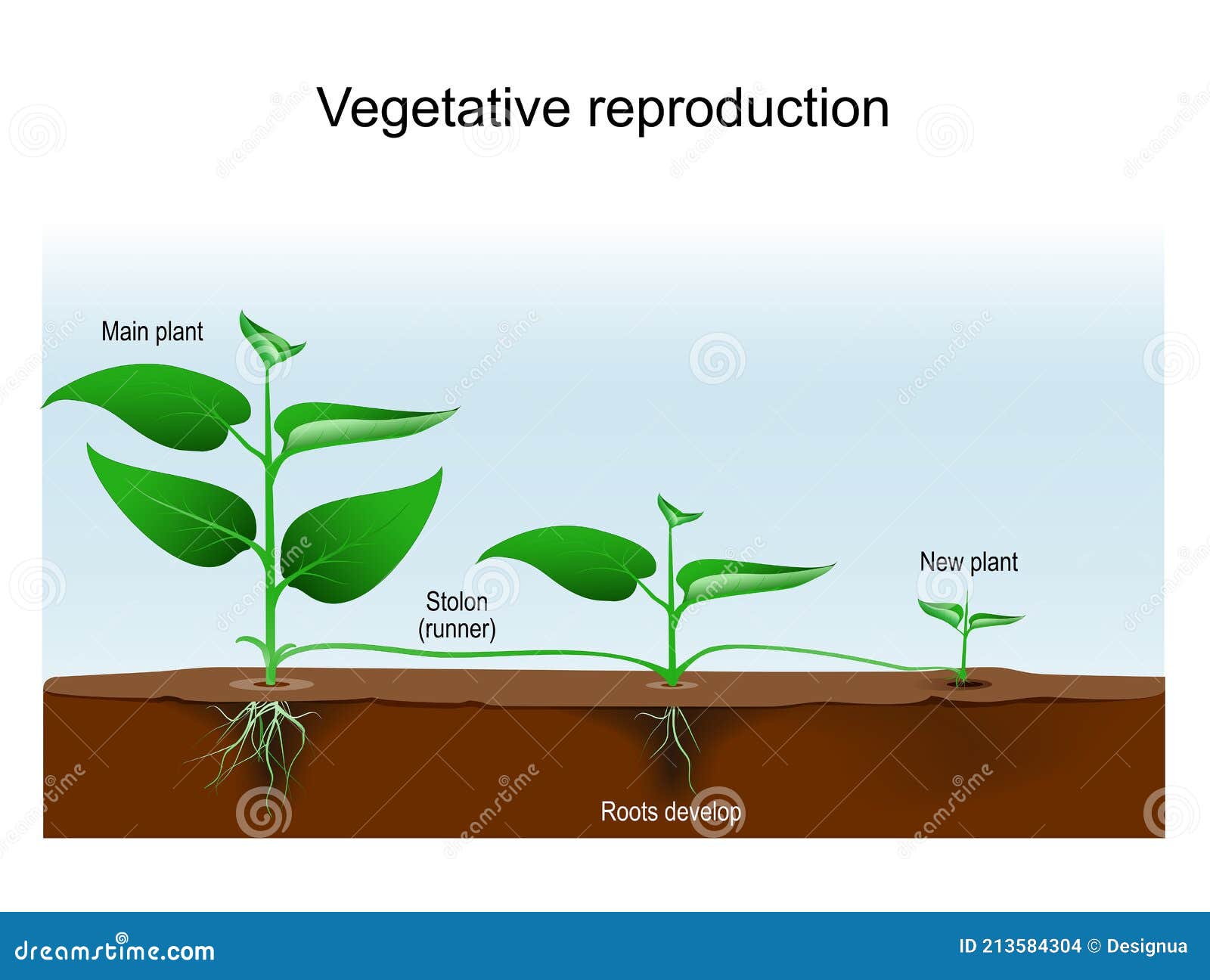
 If leaf falls damp soil, can give rise a plant. Runners strawberry reproduce stems. Plants as cacti reproduce a part detached the parent plant. detached part starts life its own. new plants produced vegetative propagation an exact copy their parent plants.
If leaf falls damp soil, can give rise a plant. Runners strawberry reproduce stems. Plants as cacti reproduce a part detached the parent plant. detached part starts life its own. new plants produced vegetative propagation an exact copy their parent plants.
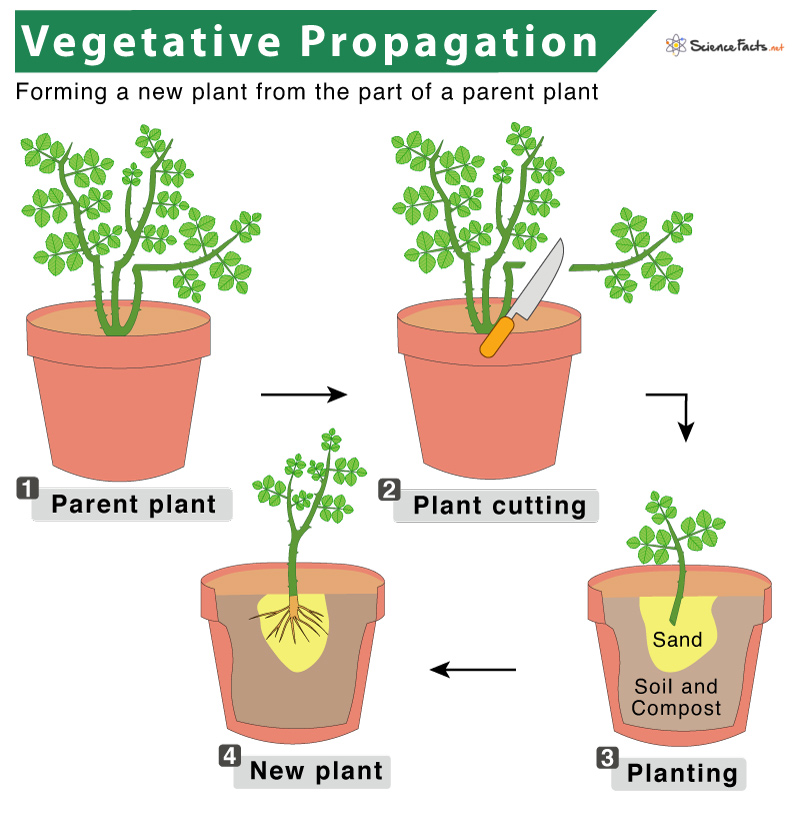
 Explore vegetative propagation plants, method asexual reproduction produces plants roots, stems, leaves. . Vegetatively propagated plants precautious bearing fruits, sometimes, flower earlier seed-propagated plants. Eg, Mango takes least 8-10 years flower grafts flower 3-4 years.
Explore vegetative propagation plants, method asexual reproduction produces plants roots, stems, leaves. . Vegetatively propagated plants precautious bearing fruits, sometimes, flower earlier seed-propagated plants. Eg, Mango takes least 8-10 years flower grafts flower 3-4 years.
 How do plants reproduce vegetatively? Open App. Solution. Vegetative reproduction plants a mode asexual reproduction. asexual reproduction, offsprings genetically identical the parent. Asexual reproduction requires only for parent.
How do plants reproduce vegetatively? Open App. Solution. Vegetative reproduction plants a mode asexual reproduction. asexual reproduction, offsprings genetically identical the parent. Asexual reproduction requires only for parent.
 Vegetables vital components a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients contributing overall health. have ever wondered how diverse nutritious plants reproduce? Let's explore fascinating world vegetable reproduction unlock mysteries their growth. Contents1 How do Vegetables Reproduce?1.1 ual Reproduction:1.2 Asexual Reproduction:2 .
Vegetables vital components a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients contributing overall health. have ever wondered how diverse nutritious plants reproduce? Let's explore fascinating world vegetable reproduction unlock mysteries their growth. Contents1 How do Vegetables Reproduce?1.1 ual Reproduction:1.2 Asexual Reproduction:2 .
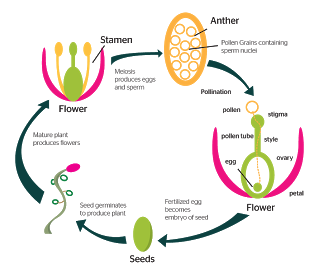 Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative Reproduction